
Technical File Management
Definition
The correct procedure (work and documentation) to be carried out in order to ensure the conformity of a motorised door is described in the relevant European Directives and Technical Standards. The main European Directive to consider is the Machinery Directive, which defines precise safety standards for all machines, including motorised doors. Below is a list of the main Directives and Standards (marked in red), as well as the Recommended Procedure for carrying out conformity assessment of motorised doors and preparing the Technical File.
Main Directives:
- 305/2011/EU - Marketing of construction products
- 2006/42/EC - Machinery Directive
- 2014/35/EU - Low Voltage Directive LVD
- 2014/30/EU - Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
- 2014/53/EU - Radio Equipment Directive (RED)
- 2011/65/EC - RoHS II Directive - Restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances
Technical Standards - Automatic Doors and Gates:
- EN 12453 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Safety in use of motorised doors, Requirements and test methods
- EN 16005 - Motorised pedestrian doors - Safety in use, Requirements and test methods
- EN 60335-2-95 - Particular requirements for vertical moving garage doors for residential use
- EN 12978 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Safety devices, Requirements and test methods
- EN 12100 - Machine safety - General principles for design - Risk assessment and risk reduction
- EN 13856-2 - Machine safety - Pressure sensitive protective devices, Part 2 General principles for design
- EN 13857 - Machine safety - Safety distances to prevent hazardous areas being reached by upper and lower limbs
- EN 13849-1 - Machine safety - Safety-related parts of control systems, Part 1: General principles for design
Product Standards - Doors and Gates:
- EN 13241 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Performance characteristics
- EN 12604 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Mechanical aspects, Requirements and test methods
- EN 12433 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Terminology, Types of doors
- EN 12424 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Resistance to wind load, Classification
- EN 12444 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Resistance to wind load, Tests and calculations
- EN 12425 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Resistance to water penetration, Classification
- EN 12489 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Resistance to water penetration, Test method
- EN 12426 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Air permeability, Classification
- EN 12427 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Air permeability, Test method
- EN 12428 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Thermal transmittance, Requirements for calculation
- EN 16034 - Pedestrian, industrial, commercial and garage doors - Performance characteristics and fire and/or smoke resistance
Standards soon to be revised:
- EN 13241 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Performance characteristics
- EN 12453 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Safety in use of powered doors, Requirements and test methods
- EN 16005 - Motorised pedestrian doors - Safety in use, Requirements and test methods
- EN 12978 - Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Safety devices, Requirements and test methods
Categories of doors contained in the Cloud area with reference to the Technical Standards
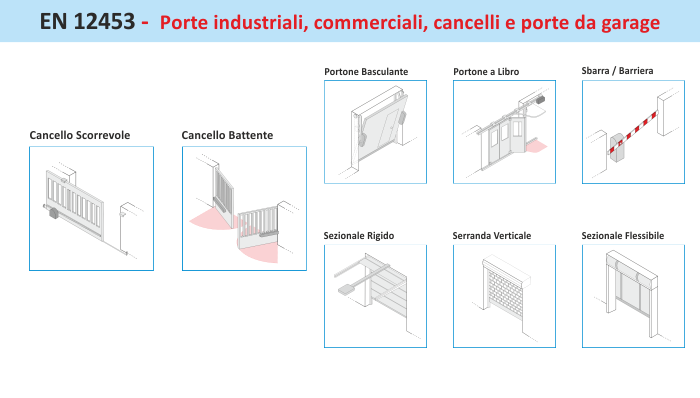
EN 12453
Industrial, commercial and garage doors and gates - Safety in use of motorised doors, Requirements and test methods
EN 60335-2-95
Particular requirements for vertical moving garage doors for residential use

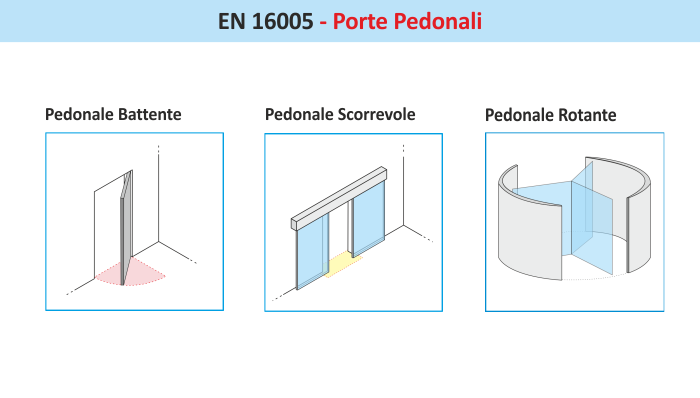
EN 16005
Motorised pedestrian doors - Safety in use, Requirements and test methods
Recommended procedure for preparing the Technical File and Conformity of motorised doors
When must the Technical File be produced?
At each new installation or when motorising a manual door.
When Extraordinary Maintenance is carried out, which includes repair and/or replacement work on various mechanical, electrical and/or electronic components and security systems.
When a request is made to "modernize" an existing installation, which includes regulatory compliance plus extraordinary maintenance work.
List of Procedures
Evaluation of the intervention and delivery of the Acceptance Report; see section Doors Management -> Acceptance Report.
If the customer confirms the intervention, the work is taken over.
After the work has been carried out, a Risk Analysis must be carried out; see section Doors Management -> Risk Analysis.
Among the various checks in the Risk Analysis, it is necessary to carry out crushing/impact force measurements; see section Doors Management -> Forces Limitation and, in case of using mobile devices on site, also the section Viewing measurements with mobile devices.
For details of the checks in the Risk Analysis, see section Index of Checks and Verifications.
To further document the Technical File it is possible to add documents and photographs; see section Doors Management -> Other linked documents.
On completion of the work, the CE marking must be applied to the door; see CE marking.
After the door has been put into
operation, must be issued to the Customer:
The Test Report; see section Risk Analysis -> Test Report (the printout is on the left menu).
The EC Declaration of Conformity; see section Doors Management -> EC Declaration.
The Maintenance Log; see section Doors Management -> Maintenance Log.
RISK ANALYSIS HANDBOOK - INDEX
Mechanical and structural risks - Checks
[01] Solidity and stability of the structure and of the support mechanical units (anti-drop)
[02] State and use of wheels/bearings/hinges or other sliding systems
[03] State and fastening of the engine or of the moving units of the leaf
[04] State and solidity of the mechanical stops of end running (leaf travel limitation)
[05] Height / modelling / highlighting of thresholds and/or floor guides
Risks caused by the movement of the leaf - Checks
[06] Minimum protection level on the main edge
[07] Safety gaps and elements to protect the opening and closing spaces
[08] Verify the impact/crushing forces with the specific instrument
Testing of auxiliary and safety devices
[09] Positioning and operation of photocells
[10] State and functioning of sensitive edges (active and/or passive)
[11] State and functioning of safety devices
[12] State and functioning of type E safety sensors / barriers
Final Checks and Documents
[13] Manual/mechanic unlocking for manual opening/closing of the leaf
[14] Positioning of the control/button of the drive unit/engine (if any)
[15] Protection of the electrical system (switch)
[16] Verify that the drive unit/engine starts its regular functioning again after a temporary power supply failure
[17] Positioning and operation of the emergency stop control (if any)
[18] State and functioning of indicator devices (flashing lights, reflectors, etc.
[19] Signs indicating unprotected residual risks and foreseeable non-compliant uses
[20] CE Marking and documentation (Declaration of Conformity, Maintenance Log, etc.)